How to Get Rid of Centipedes
If you have an active centipede infestation, follow these guidelines to learn how to get rid of house centipedes.
December 16th, 2023
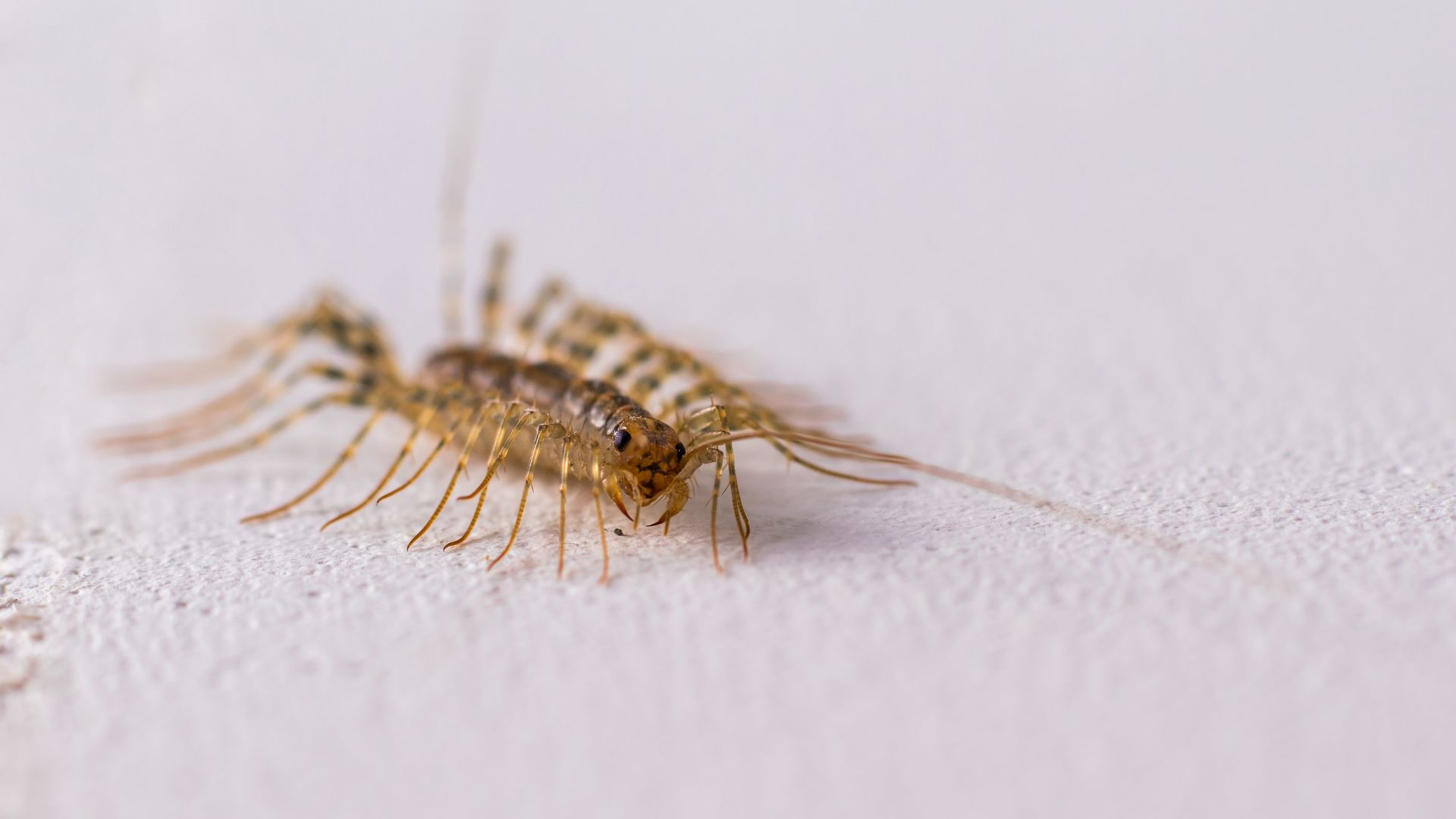
The house centipede is a common pest in many parts of the United States. Unlike most other centipedes, the House Centipede lives its entire life inside a building.
Each segment of these creepy crawlies bodies has one pair of legs, which is why House Centipedes are known as "100 leggers".
This pest prefers to live in damp spaces such as cellars, closets, and bathrooms. They can also be found in attics (during the warmer months) and unexcavated areas under the house. Eggs are laid in these same damp places and behind baseboards or beneath bark on firewood.
Other species prefer damp conditions under stones, boards, leaves, or in mulch around plantings, and rarely make their way indoors. This article will discuss how to identify house centipedes, and how to get rid of them when they infest your home.

How to Kill Centipedes
Prevention is the First Step to Getting Rid of House Centipedes
Centipedes can be prevented from gaining entry into buildings by sealing and caulking gaps around siding, windows, doors, pipes, wires, and other structural voids.
An easy-to-spray foam spray like Pur Black NF Foam has a closed-cell foam that seals openings and voids to prevent insects and rodents from entering buildings.
House centipedes can be controlled indoors by eliminating their harborage areas. Removal of centipedes' habitats, including trash, rocks, boards, compost piles, and other hiding places around the structure, would reduce the population.
Key Takeaway
Centipedes can be found inside homes and out. To eliminate them successfully, we recommend treating the interior and exterior of your home.
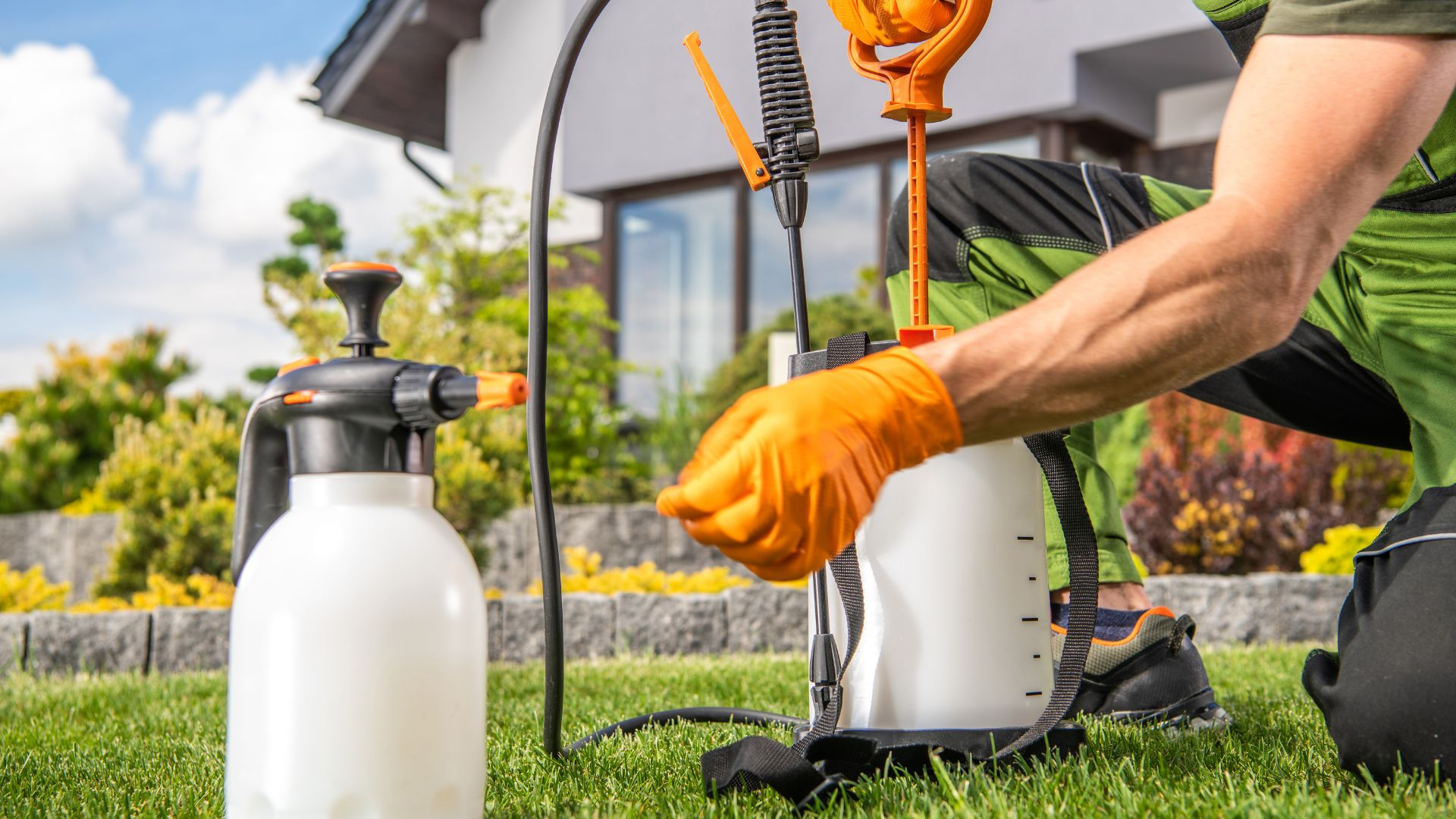

Apply a Residual Concentrate to Eliminate Centipedes
Avesta CS, Cyzmic CS, or Cyper WSP may be applied inside or outside and are residual insecticides. These products are sprayed along cracks and crevices, entry points, and baseboards to discourage centipede activity.
Apply these residual insecticides in a 3-foot to 10-foot band around the structure's perimeter. Also, spray into harborage sites and around potential entry points. Both products will give you a long-term residual-about three months and a good spray for all surfaces.
Liquid applications can be introduced into cracks and crevices along baseboards and into other potential hiding places.
In addition to the recommended residual insecticides, you may also use an aerosol like PT 221L Aerosol or Cy-Kick Crack and Crevice Aerosol.
Spray around doors and windows and other places where these pests may enter the premises. This aerosol has a crack and crevice tip to apply in the very small cracks and crevices, where the liquid spray can not go.
As an extra measure, use residual dust such as D-Fense Dust. Dust attic areas and under baseboards. A recommended dust for attic areas would be D-Fense Dust with a hand duster or garden duster.
Pur Black NF is Pur Black Gun Foam in a convenient can with a nozzle. Pur Black NF is a straw-dispensed foam that expands, bonds, and seals to stop the passage of air, gases, water, dust, fibers, sound, rodents, pests, radon, and odors.
Products to Use to Get Rid of a Centipede Infestation
1. Use a Vacuum to Suck Up Centipedes
House centipedes that are difficult to reach with other methods can be sucked up with a powerful vacuum.
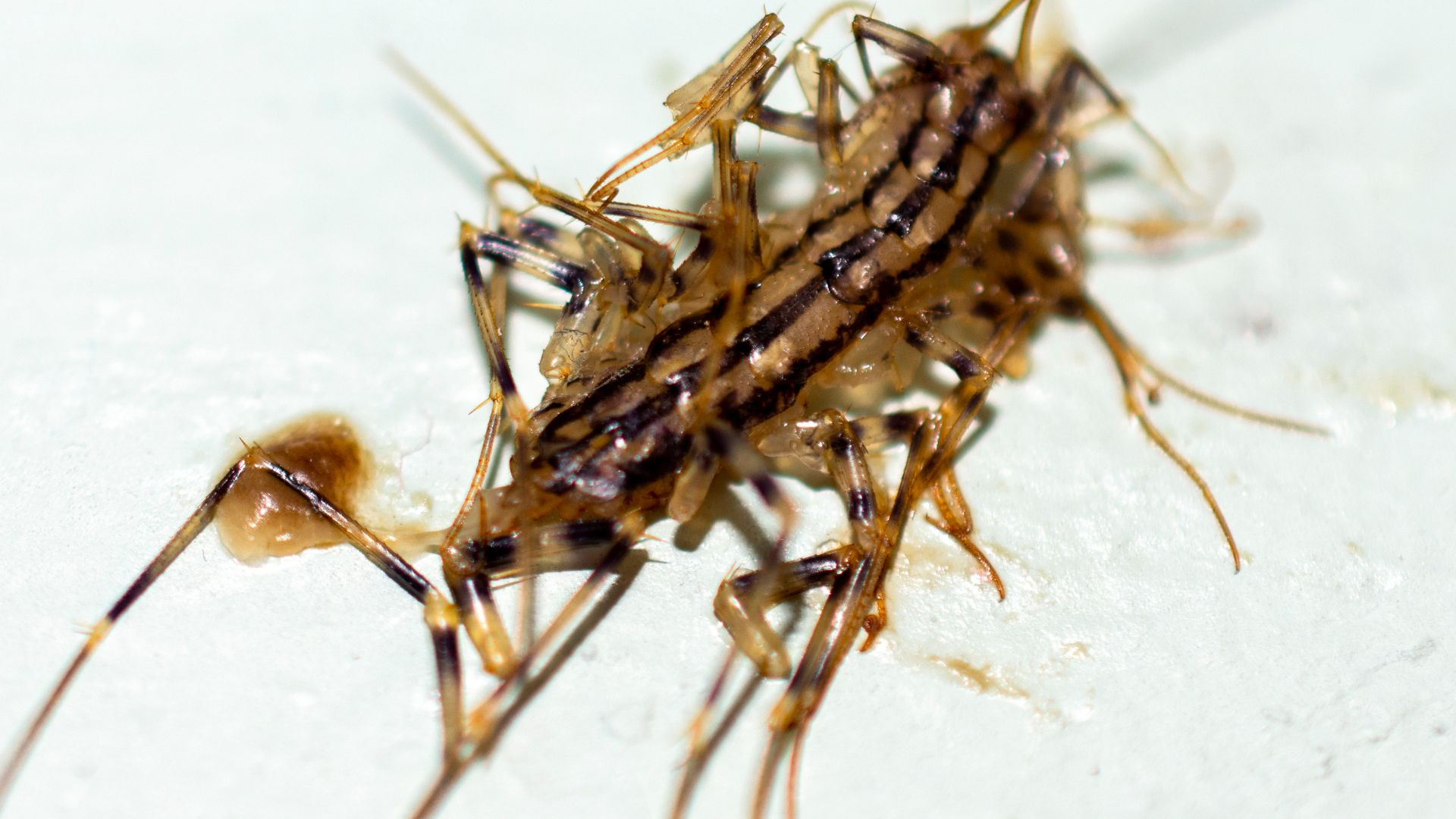

2. Place Sticky Traps to Kill Centipedes
When house centipedes come out to look for nourishment, sticky traps set strategically about your home can catch them.
3. Use Pesticide Spray
To get rid of house centipedes and protect your home from re-infestation, apply a pesticide spray.
4. Pesticide Granules for Centipede Control.
Granules can be applied on the outside of your home to kill house centipedes looking for a way in. Granules are fantastic for eliminating these crawling pests and preventing future infestations.
5. Natural Remedies to Discourage Centipedes
Centipedes of all kinds are rarely hazardous and represent no real threat to people, therefore dealing with them organically is extremely simple. You can use a dustpan or broom to remove centipedes from your home.
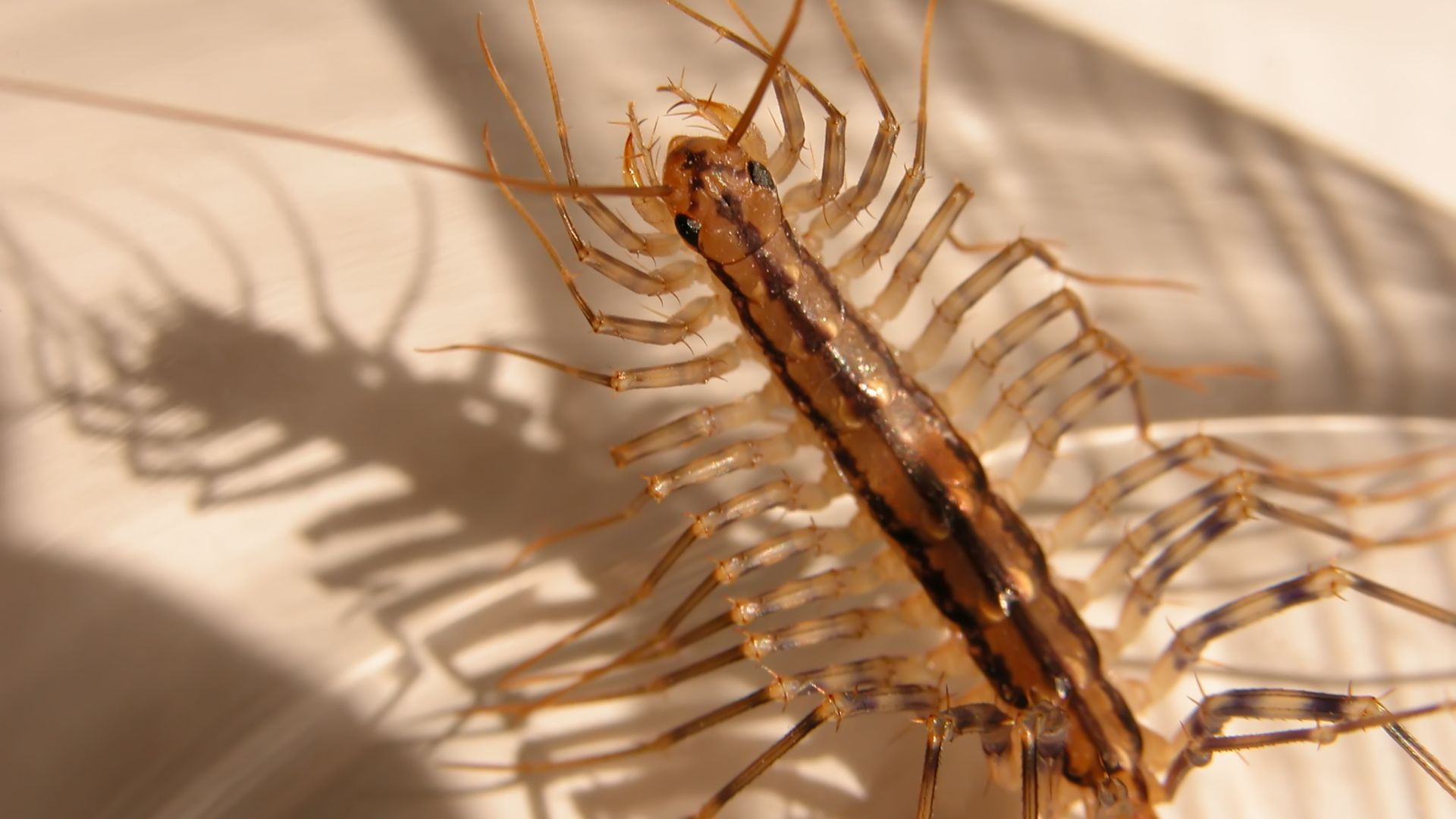

Identify House Centipedes
-
The house centipede is grey-yellow with three stripes down the back and has very long legs banded with white.
-
Centipedes (100 legs) are usually brownish and elongated. These arthropods are flattened, with many different body segments.
-
They have one pair of legs attached to most of these body segments; they can have 177 pairs of legs.
-
Centipedes differ from millipedes; millipedes have two pairs of legs on most segments and bodies which are not flattened. The last pair of legs is nearly twice the length of the body of adult females.
-
These arthropods are between 1-6 inches.
-
The house centipede's body is usually only 1 to 1 1/2 inches long at the most, but its 15 pairs of legs make it seem much larger.
-
The largest centipedes are found in the Southwest.
Centipede Damage and Bites
House Centipedes are predatory insects that hunt both indoors and outdoors. Only one species, the house centipede, is capable of reproducing and maintaining populations indoors; the others may wander in by chance but cause no harm.
These pests do not represent a threat to people in general. They can and will bite if they are really agitated, and the toxin they inject can induce a reaction in a small percentage of humans who are allergic to it.
Otherwise, the pain is comparable to that of a bee sting, and this creature uses it as a last-option weapon. A physician should be consulted if the house centipede bites have penetrated the skin.
House Centipedes do not typically damage household furnishings or get into food supplies.
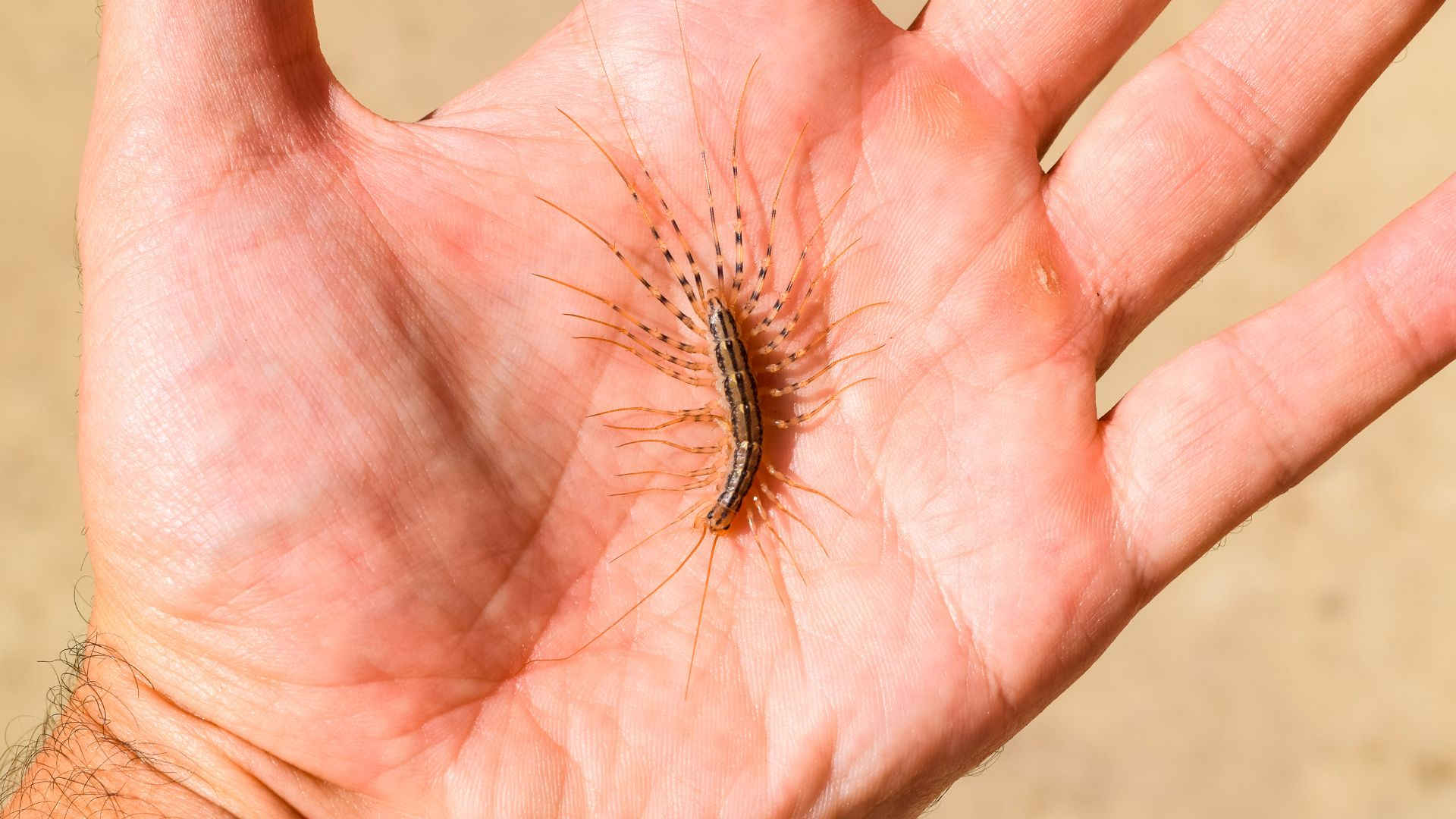

Centipede Biology
These pests typically overwinter outdoors; in the summer, and can lay 35 eggs or more in or on the soil.
Newly hatched centipedes have four pairs of legs; during subsequent molts. They progressively increase the number of legs until they become an adult. Adults of many species live a year and some as long as five to six years.

Inspect
Where Centipedes are Found
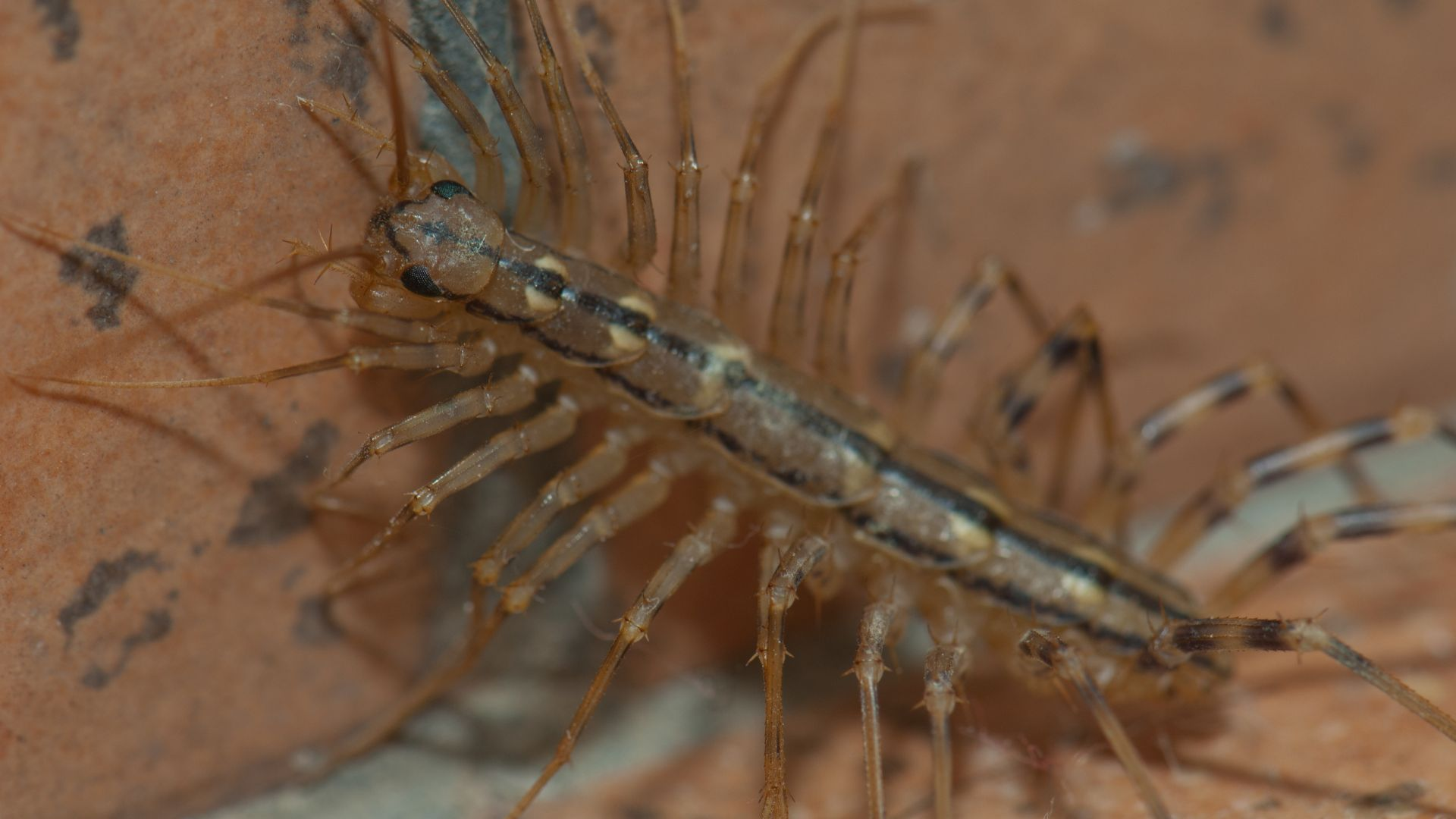
Because of their evasive behavior, a house centipede infestation might be difficult to detect. House centipedes spend the majority of their days in damp, gloomy places.
How to Spot A House Centipede Infestation
If you want to examine your home for house centipedes, start looking in any location that has had water problems in the past. Look under sinks and in the basement for house centipedes to begin your search.
Centipedes usually live outside, but you can find them inside as well. When they are outdoors, they typically live in damp areas such as under leaves, stones, boards, tree bark, or mulch around outdoor plantings. If they are around the foundation of the house, they may wander inside.
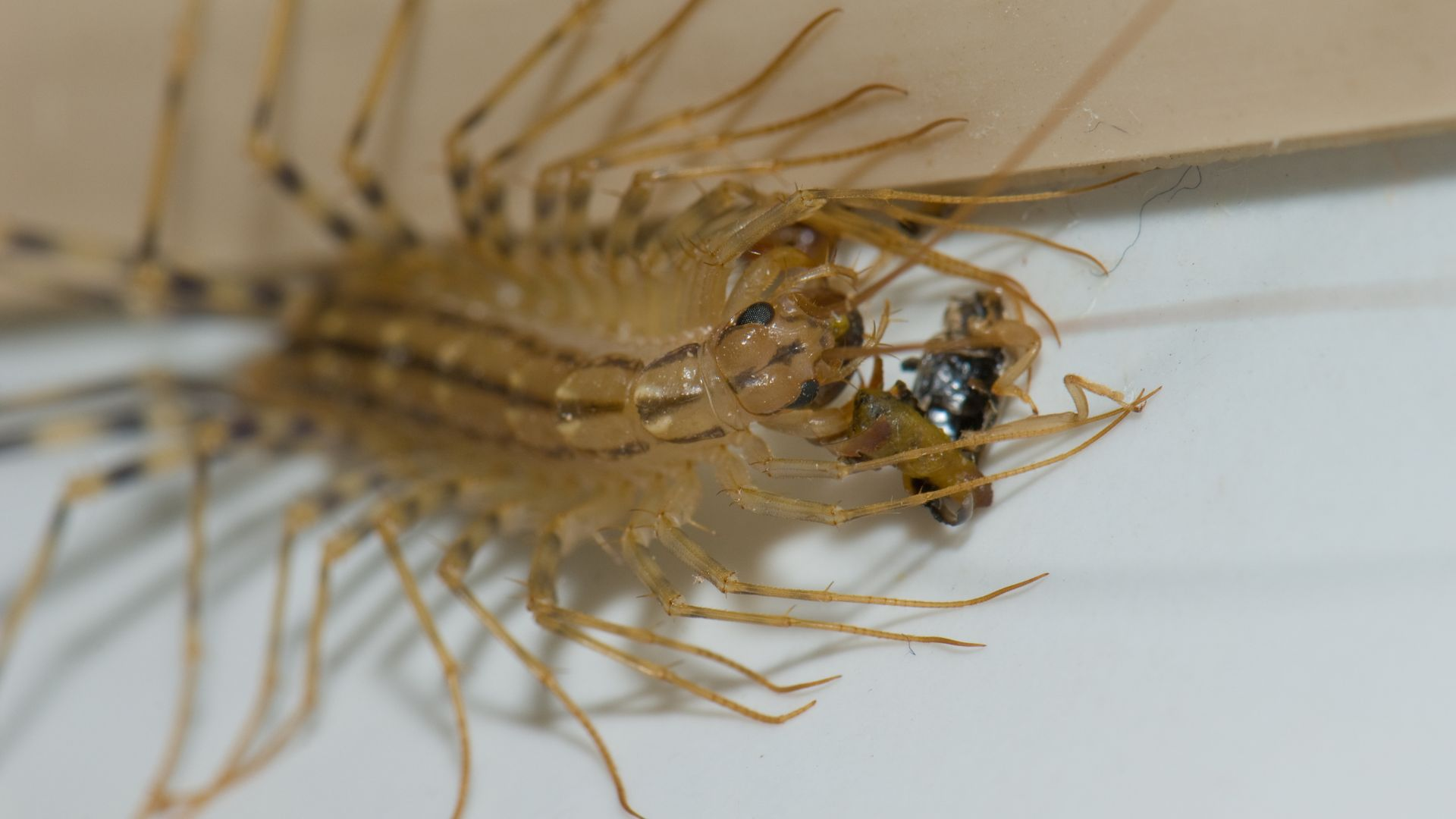

House Centipedes Feed on Spiders and Insects
House centipedes are most active at night time, so wait till the sun goes down to begin your inspection. Start by looking in places where wetness is most likely to occur, such as the bathroom, kitchen, or basement. Because House Centipedes prefer to feed on insects, spiders, and other pests, you will likely find them in those rooms. Keep in mind that they may run quite rapidly and on their rear legs!
Prevention: Long-Term Centipede Control
Long-term control of Centipedes is achieved by the removal of breeding sites. Remove any mulch, leaves, wood heaps, or other breeding areas. Spray all of the house's entry points, as well as a 3-6 foot radius surrounding it. Spray door thresholds, baseboards, and any other areas where they have been spotted on the inside.
Tips to Prevent Centipede Infestations
There are various things you can do to prevent future infestations in your house.
1. Reduce Moisture Levels
These creatures love to live in moist, high-humidity conditions. Repair any water leaks in your home, use dehumidifiers, and utilize exhaust fans in bathrooms and attics to reduce excess moisture in these areas. Also, make sure floor drains are clear of blockage to ensure water drainage. This will help you eliminate house centipedes and prevent them from coming back.
2. Chronic Infestations
In addition, to the Avesta CS or LambdaStar UltraCap SC spray, use D-Fense Dust inside the wall voids and seal cracks and other entry points with Pur Black NF Foam.

3. Remove Food Sources
Centipedes eat insects and spiders, thus controlling insects and other pests inside your home will also control them. Unlike millipedes, centipedes do not feed on grass clippings and leaf litter.

4. Block Entryways
To prevent House Centipedes and keep other insect pests out, seal holes in cement block walls, crevices, crawl spaces, and gaps around the outside of your home. Insects are kept out by repairing tears in screens and installing weather stripping to doors and windows.
5. Spray Insecticides
To build a barrier that helps keep unwanted pests out, apply insecticides to door and window casings, along baseboards, and outside the perimeter of your home.
6. Use Sticky Traps to Get Rid of House Centipedes
Set out these traps to catch them as they hunt at night. These pesticide-free traps are simple to set up: simply unfold them, remove the release paper, and place them in areas where centipedes and other pests are known to congregate.
How to Get Rid of Centipedes
If you have an active centipede infestation, follow these guidelines to learn how to get rid of house centipedes.
Where Centipedes are Found
Centipedes usually live outside, but the House Centipede you can find inside as well. Centipedes typically live outdoors in damp areas such as under leaves, stones, boards, tree bark, or mulch around outdoor plantings. If they are around the foundation of the house, they may wander inside. Most centipedes are active at night.
Identify House Centipedes
- Centipedes (100 legs) are usually brownish and elongated. Centipedes are flattened, with many different body segments.
- Centipedes have one pair of legs attached to most of these body segments; they can have 177 pairs of legs.
- Centipedes differ from millipedes; millipedes have two pairs of legs on most segments and bodies which are not flattened.
- Centipedes are between 1-6 inches, and the House Centipede is 1-1/12 inches.
How to Kill Centipedes
Prevention is the first Step
Centipedes can be prevented from gaining entry into buildings by sealing and caulking gaps around siding, windows, doors, pipes, wires, and other structural voids. An easy to spray foam spray like Pur Black NF Foam has a closed-cell foam that seals openings and voids from insects and rodents from entering buildings.
Removal of centipedes habitats, including trash, rocks, boards, compost piles, and other hiding places around the structure, would reduce the population. The House Centipede will prefer to live in damp areas like basements, bathrooms, behind baseboards, or attics. House centipedes can be controlled indoors by eliminating their harborage areas. Where possible and using a vacuum to remove exposed centipedes.
Key Takeaway
Centipedes can be found inside homes and out so treating the inside and outside perimeter is recommended.
- Avesta CS and Cyper WSP may be applied inside or outside and are residual insecticides. These products are sprayed along cracks and crevices, entry points, and baseboards and discourage centipedes activity.
- Apply these residual insecticides in a 3- to 10-foot band around the structure's perimeter. Also, spray into harborage sites and around potential entry points. Both products will give you long term residual-about three months and a good spray for all surfaces.
- Liquid applications can be introduced into cracks and crevices along baseboards and into other potential hiding places.
- In addition to the recommended residual insecticides, you may also use an aerosol like PT 221L Aerosol or Cy-Kick Crack and Crevice Aerosol
- Spray around doors and windows and other places where these pests may enter premises. This aerosol has a crack and crevice tip to apply in the very small cracks and crevices, where the liquid spray can not go.
- As an extra measure, use residual dust such as D-Fense Dust. Dust attic areas and under baseboards. A recommended dust for attic areas would be D Fense Dust with a hand duster or garden dusters.
- Pur Black NF is Pur Black Gun Foam in a convenient can with a nozzle. Pur Black NF is a straw dispensed foam that expands, bonds, and seals to stop the passage of air, gases, water, dust, fibers, sound, rodents, pests, radon, and odors.
House Centipedes
The house centipede is a common pest in many parts of the United States. Unlike most other centipedes, the House Centipede lives its entire life inside a building.
The house centipede is grey-yellow with three stripes down the back and has very long legs banded with white. The largest centipedes are found in the Southwest. This centipede's body is usually only 1 to 1 1/2 inches long at the most, but it's 15 pairs of legs make it seem much larger. The body is grayish-yellow with three dark stripes extending along the full length of the back.
The House Centipede will prefer to live in damp areas such as cellars, closets, bathrooms. They can also be found in attics (during the warmer months) and unexcavated areas under the house. Eggs are laid in these same damp places and behind baseboards or beneath bark on firewood.
Centipede Damage and Bites
Larger centipedes can bite if they are injured, with slight swelling. A physician should be consulted if the bite has penetrated the skin. The centipede is beneficial, eating other insects. Centipedes do not damage food supplies or household furnishings.
Centipede Biology
Centipedes typically overwinter outdoors; in the summer, centipedes lay 35 eggs or more in or on the soil. Newly hatched centipedes have four pairs of legs; during subsequent molts. The centipede progressively increases the number of legs until becoming an adult. Adults of many species live a year and some as long as five to six years.
More Centipede Control Products
Written by our resident pest control expert Ken Martin.










